Thoracic osteochondrosis is a chronic disease, which is based on the degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the intervertebral cartilage disks, which leads to reactive changes in the vertebrae and surrounding soft tissues. The disease is widespread and affects mainly people of working age (25-45 years).
Thoracic degenerative disc disease occurs much less frequently than lumbar or cervical. This is because this area of the spine is less static and engine load than the others. However, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is much more difficult to diagnose, because it most often occurs, simulating disease of the lungs, heart, organs of the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes and risk factors
Currently, the exact causes of thoracic degenerative disc disease have not been established. The experts proposed many theories (infectious-allergic, genetic, mechanical, hormonal, vascular), but none of them give a clear and complete explanation of pathological changes in the spine and lead to degeneration of tissues. Most likely, the pathological mechanism of the development of thoracic osteochondrosis simultaneously involved in a number of different factors. But the main value belongs to the long-static-dynamic overload of the spine segment.
Causative factors, such as overload are:
- abnormalities in the structure of the spine;
- asymmetrical arrangement of joint cracks in the intervertebral joints;
- congenital narrowing of the spinal canal;
- spondylogenic muscular (myofascial, mirrored) and/or somatic (mirrored, arising on a background of a number of diseases of the blood vessels and internal organs) pain;
- long-term exposure of the spine to vibration, for example, motor vehicle drivers;
- physical stress;
- obesity;
- Smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle (lack of exercise);
- psycho-social factors.
The mobility of the spine is provided by the intervertebral discs, which also play a cushioning role. The middle is elastic nucleus pulposus, which in large quantities is water. Osteochondrosis of the core begins to lose water, as a result of demineralization of polysaccharides. Over time, the core is flat, and with it, he flattens and the intervertebral disc. Under the influence of mechanical load on the fibrous ring bulges, a process called protrusion. Later drive cracks through which fall the pieces of the nucleus pulposus, i.e., the formation of a herniated disc.
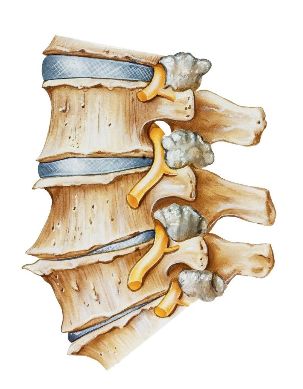
Reduction of disc height leads to a convergence of the adjacent vertebrae, disruption of the anatomy of the facet joints. All of this triggers a reactive inflammation of the facet joints and surrounding soft tissues. In addition, the convergence of the vertebral body accompanied by stretching and joint capsules, and the affected segment of the spine becomes unstable. Vertebrae the to get excessive movement, which can become a cause of infringement of spinal roots and radicular syndrome.
On the background of osteochondrosis of the breast gradually grow into the bone tissue of the vertebra form a bony growths (osteophytes). They can also cause nerve root compression syndrome or myelopathy (spinal cord compression).
Classification
Classification of thoracic osteochondrosis lies posindromnoy principle. Depending on which nerve structures, affect the structure of the spine affected, identify the following syndromes:
- compression – the basis for its development lies in the tension, the deformation or compression of the nerve root, part of spinal cord or vascular, depending on what develops in the spinal, vascular or radicular syndromes;
- reflex – is associated with reflex excitement of the innervated muscles, degenerative and vascular disorders;
- bioadaptive.
Symptoms of thoracic degenerative disc disease
The main symptoms of thoracic degenerative disc disease is pain. In most cases it is a dull modest.
Long-term stimulation of the spinal root cause of the innervation of the internal organs. Depending on the level of the lesion, thoracic osteochondrosis can occur under the guise of somatic diseases.
| The level of damage | - Innervated organs | Clinical symptoms |
| C7-Th1 | Hand, wrist, hands, trachea, esophagus | Pain in the arms and hands, asthma |
| Th2-Th3 | The heart, pericardium, coronary arteries | Coronary heart disease, arrhythmia |
| Th4-Th5 | Bronchi, lungs, pleura, the mammary glands, nipples | Bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy>[!@#$], asthma |
| Th5-Th6 | The common bile duct, the gallbladder | Bile stone disease, a violation of the process of digestion of fats |
| Th6-Th7 | Liver, solar plexus | Disorders of the liver |
| Th7-Th8 | Stomach | Dyspepsia, gastritis, gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer |
| Th8-Th9 | Duodenum, pancreas | Digestion and chair, duodenitis, inflammation of the pancreas |
| Th9-Th10 | Spleen, the solar plexus | Hiccups, respiratory disorders |
| Th10-Th11 | The adrenal glands | Allergic reactions, weakened immunity |
| Th11-Th12 | Kidney | Pyelonephritis, urinary stone disease |
| Th12-L1 | The kidneys and ureters | Urinating |
In this regard, the most common symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are:
- pain in the chest (behind the sternum, at the side, behind, intercostal space) – can be both acute and aching, dull, often radiating to the arm;
- pain in the epigastric region – arise regardless of the nature of power, the characteristics of the diet; often combined with heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the right upper quadrant – increase by changing the position of the patient's body, sneezing, cough;
- pain in the lumbar region – to simulate an attack of renal colic, often associated with dysuric disorders.
Compression of the nerve roots of the patient's thoracic osteochondrosis develops an attack of intercostal neuralgia. It is characterized by the occurrence of acute pain on one side of the chest (thoracalgia). Pain surrounded by nature and is applied to, of course, one of the intercostal nerves of the spine to the sternum. Patients describe them as "electric shocks" or "cross". The pain can radiate in the area in the epigastrium, sternum area, shoulder, arm, and combined with some other symptoms (local heavy sweating, paleness or redness of the skin), which is associated with damage to the sympathetic fibers of intercostal nerves.
For the intercostal neuralgia characteristic paroxysms of pain, which lasts for several seconds to several minutes. During the attack the pain becomes unbearable. Trying to somehow alleviate their condition, the patients to freeze in a certain position of the body, avoid taking deep breaths, coughing, sneezing, changing.
Away from the pain attack patients observed paresthesia (subjective violations of skin sensitivity in the form of pins and needles, tickling, pricking with needles) during intercostal space.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis is carried out on the basis of information objective examination of the patient, laboratory and instrumental examination, including:
- General blood count (mild leukocytosis, increased ESR);
- serum electrolytes (low levels of calcium);
- urine;
- biochemical analysis of blood;
- x-ray examination of the thoracic spine (detected by the flattening of the intervertebral disc, the deformation of the end plates of the adjacent vertebra, the transition to the adjacent vertebrae relative to each other);
- scintigraphy of the spine (to expose the process of active mineralization of bone tissue of the vertebral bodies);
- myelography;
- computer and magnetic resonance tomography.
Breast low back pain requires differential diagnosis the following diseases and pathological conditions:
- dishormonal spondylopathy;
- spondylolisthesis;
- inflammation;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- osteomyelitis of the spine;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- neoplastic processes (metastatic or primary tumors of the chest);
- fractures of the spine;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic pancreatitis, gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome);
- diseases of the genitourinary system (urolithiasis, pyelonephritis);
- cardiovascular disease (coronary heart disease, arrhythmia).
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is carried out in ambulatory conditions. When expressed pain syndrome patients 2-3 days of rest is prescribed. Shown traction of the affected segment of the spine, which helps to eliminate compression of the nerve root and thus prevent pain. When expressed pain syndrome carried out infiltration of soft tissues 2% solution of novocaine. A short course may be prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
The system in the complex treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis are also included:
- antihistamines;
- b-vitamins;
- tranquilizers;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- manual therapy.
After improvement the patient was sent to physical therapy sessions. Regular performance of physical exercise in breast osteochondrosis promotes the formation of well-developed muscular system, which allows to keep the spine in the correct physiological position, to remove the excessive static loads.
Of great importance for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is given in regular moderate exercise (swimming, yoga, tai Chi), the normalization of weight. Jumping, running, weight lifting and other sports, the increased load on the spine, is contraindicated.
Surgical treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis are shown only if significant spinal cord compression. In such cases, depending on the readers as follows:
- stabilization of the spinal segment;
- replacement of the affected disc with an artificial implant;
- laser reconstruction plate;
- puncture of the vaporization of the affected disc;
- a micro discectomy.
Possible consequences and complications
Prolonged irritation or compression of the nerve roots can trigger the development of somatic diseases of the chest, the upper part of the digestive system, the kidneys. The greatest danger thoracic osteochondrosis is the heart muscle.
Also the effects of thoracic degenerative disc disease can be a disease of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, pancreas, gall bladder, lungs, and the formation of intervertebral hernia.
Forecast
Thoracic osteochondrosis is characterized by undulating course, where remission is associated with exacerbations. Timely initiation of treatment, the patient will comply with all recommendations of the doctor, concerning both disease treatment and lifestyle changes, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
Prevention breast osteoarthritis includes:
- normalization of weight;
- Smoking cessation;
- active way of life.
































